Hook原理——状态Hook

-
function 类型的 fiber 节点, 它的处理函数是 updateFunctionComponent, 其中再通过 renderWithHooks 调用 function.
-
在 function 中, 通过 Hook Api(如: useState, useEffect)创建 Hook 对象.
状态 Hook 实现了状态持久化(等同于 class 组件维护 fiber.memoizedState).
副作用 Hook 则实现了维护 fiber.flags,并提供副作用回调(类似于 class 组件的生命周期回调)
-
多个 Hook 对象构成一个链表结构, 并挂载到 fiber.memoizedState 之上.
-
fiber 树更新阶段, 把 current.memoizedState 链表上的所有 Hook 按照顺序克隆到 workInProgress.memoizedState 上, 实现数据的持久化.
创建 Hook
在 fiber 初次构造阶段, useState 对应源码 mountState, useReducer 对应源码 mountReducer
mountState:
function mountState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
// 1. 创建hook
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
if (typeof initialState === 'function') {
initialState = initialState();
}
// 2. 初始化hook的属性
// 2.1 设置 hook.memoizedState/hook.baseState
// 2.2 设置 hook.queue
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
const queue = (hook.queue = {
pending: null,
dispatch: null,
// queue.lastRenderedReducer是内置函数
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer,
lastRenderedState: (initialState: any),
});
// 2.3 设置 hook.dispatch
const dispatch: Dispatch<
BasicStateAction<S>,
> = (queue.dispatch = (dispatchAction.bind(
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber,
queue,
): any));
// 3. 返回[当前状态, dispatch函数]
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}mountReducer:
function mountReducer<S, I, A>(
reducer: (S, A) => S,
initialArg: I,
init?: I => S,
): [S, Dispatch<A>] {
// 1. 创建hook
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
let initialState;
if (init !== undefined) {
initialState = init(initialArg);
} else {
initialState = ((initialArg: any): S);
}
// 2. 初始化hook的属性
// 2.1 设置 hook.memoizedState/hook.baseState
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
// 2.2 设置 hook.queue
const queue = (hook.queue = {
pending: null,
dispatch: null,
// queue.lastRenderedReducer是由外传入
lastRenderedReducer: reducer,
lastRenderedState: (initialState: any),
});
// 2.3 设置 hook.dispatch
const dispatch: Dispatch<A> = (queue.dispatch = (dispatchAction.bind(
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber,
queue,
): any));
// 3. 返回[当前状态, dispatch函数]
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
mountState 和 mountReducer 逻辑简单: 主要负责创建 hook, 初始化 hook 的属性, 最后返回[当前状态, dispatch 函数].
唯一的不同点是 hook.queue.lastRenderedReducer:
- mountState 使用的是内置的 basicStateReducer
function basicStateReducer<S>(state: S, action: BasicStateAction<S>): S {
return typeof action === "function" ? action(state) : action;
}- mountReducer 使用的是外部传入自定义 reducer
可见 mountState 是 mountReducer 的一种特殊情况, 即 useState 也是 useReducer 的一种特殊情况, 也是最简单的情况.
useState 可以转换成 useReducer:
const [state, dispatch] = useState({ count: 0 });
// 等价于
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(
function basicStateReducer(state, action) {
return typeof action === "function" ? action(state) : action;
},
{ count: 0 }
);
// 当需要更新state时, 有2种方式
dispatch({ count: 1 }); // 1.直接设置
dispatch((state) => ({ count: state.count + 1 })); // 2.通过回调函数设置可见, useState 就是对 useReducer 的基本封装, 内置了一个特殊的 reducer(后文不再区分 useState, useReducer, 都以 useState 为例).创建 hook 之后返回值[hook.memoizedState, dispatch]中的 dispath 实际上会调用 reducer 函数.
状态初始化
在useState(initialState)函数内部, 设置hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;, 初始状态被同时保存到了hook.baseState,hook.memoizedState中.
- hook.memoizedState: 当前状态
- hook.baseState: 基础状态, 作为合并 hook.baseQueue 的初始值(下文介绍).
最后返回[hook.memoizedState, dispatch], 所以在 function 中使用的是 hook.memoizedState.
状态更新
有如下组件
import { useState } from "react";
export default function App() {
const [count, dispatch] = useState(0);
return (
<button
onClick={() => {
dispatch(1);
dispatch(3);
dispatch(2);
}}
>
{count}
</button>
);
}初次渲染时 count = 0, 这时 hook 对象的内存状态如下:

点击 button, 通过 dispatch 函数进行更新, dispatch 实际就是 dispatchAction:
function dispatchAction<S, A>(
fiber: Fiber,
queue: UpdateQueue<S, A>,
action: A,
) {
// 1. 创建update对象
const eventTime = requestEventTime();
const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber); // Legacy模式返回SyncLane
const update: Update<S, A> = {
lane,
action,
eagerReducer: null,
eagerState: null,
next: (null: any),
};
// 2. 将update对象添加到hook.queue.pending队列
const pending = queue.pending;
if (pending === null) {
// 首个update, 创建一个环形链表
update.next = update;
} else {
update.next = pending.next;
pending.next = update;
}
queue.pending = update;
const alternate = fiber.alternate;
if (
fiber === currentlyRenderingFiber ||
(alternate !== null && alternate === currentlyRenderingFiber)
) {
// 渲染时更新, 做好全局标记
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass = didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate = true;
} else {
// ...省略性能优化部分, 下文介绍
// 3. 发起调度更新, 进入`reconciler 运作流程`中的输入阶段.
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);
}
}-
创建 update 对象, 其中 update.lane 代表优先级(可回顾 fiber 树构造(基础准备)中的 update 优先级).
-
将 update 对象添加到 hook.queue.pending 环形链表. 环形链表的特征: 为了方便添加新元素和快速拿到队首元素(都是 O(1)), 所以 pending 指针指向了链表中最后一个元素.
-
发起调度更新: 调用 scheduleUpdateOnFiber, 进入 reconciler 运作流程中的输入阶段.
本示例中虽然同时执行了 3 次 dispatch, 会请求 3 次调度, 由于调度中心的节流优化, 最后只会执行一次渲染
在 fiber 树构造(对比更新)过程中, 再次调用 function, 这时 useState 对应的函数是 updateState
function updateState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
return updateReducer(basicStateReducer, (initialState: any));
}实际调用 updateReducer.
在执行 updateReducer 之前, hook 相关的内存结构如下:

执行:
function updateReducer<S, I, A>(
reducer: (S, A) => S,
initialArg: I,
init?: I => S,
): [S, Dispatch<A>] {
// 1. 获取workInProgressHook对象
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
const queue = hook.queue;
queue.lastRenderedReducer = reducer;
const current: Hook = (currentHook: any);
let baseQueue = current.baseQueue;
// 2. 链表拼接: 将 hook.queue.pending 拼接到 current.baseQueue
const pendingQueue = queue.pending;
if (pendingQueue !== null) {
if (baseQueue !== null) {
const baseFirst = baseQueue.next;
const pendingFirst = pendingQueue.next;
baseQueue.next = pendingFirst;
pendingQueue.next = baseFirst;
}
current.baseQueue = baseQueue = pendingQueue;
queue.pending = null;
}
// 3. 状态计算
if (baseQueue !== null) {
const first = baseQueue.next;
let newState = current.baseState;
let newBaseState = null;
let newBaseQueueFirst = null;
let newBaseQueueLast = null;
let update = first;
do {
const updateLane = update.lane;
// 3.1 优先级提取update
if (!isSubsetOfLanes(renderLanes, updateLane)) {
// 优先级不够: 加入到baseQueue中, 等待下一次render
const clone: Update<S, A> = {
lane: updateLane,
action: update.action,
eagerReducer: update.eagerReducer,
eagerState: update.eagerState,
next: (null: any),
};
if (newBaseQueueLast === null) {
newBaseQueueFirst = newBaseQueueLast = clone;
newBaseState = newState;
} else {
newBaseQueueLast = newBaseQueueLast.next = clone;
}
currentlyRenderingFiber.lanes = mergeLanes(
currentlyRenderingFiber.lanes,
updateLane,
);
markSkippedUpdateLanes(updateLane);
} else {
// 优先级足够: 状态合并
if (newBaseQueueLast !== null) {
// 更新baseQueue
const clone: Update<S, A> = {
lane: NoLane,
action: update.action,
eagerReducer: update.eagerReducer,
eagerState: update.eagerState,
next: (null: any),
};
newBaseQueueLast = newBaseQueueLast.next = clone;
}
if (update.eagerReducer === reducer) {
// 性能优化: 如果存在 update.eagerReducer, 直接使用update.eagerState.避免重复调用reducer
newState = ((update.eagerState: any): S);
} else {
const action = update.action;
// 调用reducer获取最新状态
newState = reducer(newState, action);
}
}
update = update.next;
} while (update !== null && update !== first);
// 3.2. 更新属性
if (newBaseQueueLast === null) {
newBaseState = newState;
} else {
newBaseQueueLast.next = (newBaseQueueFirst: any);
}
if (!is(newState, hook.memoizedState)) {
markWorkInProgressReceivedUpdate();
}
// 把计算之后的结果更新到workInProgressHook上
hook.memoizedState = newState;
hook.baseState = newBaseState;
hook.baseQueue = newBaseQueueLast;
queue.lastRenderedState = newState;
}
const dispatch: Dispatch<A> = (queue.dispatch: any);
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}-
调用 updateWorkInProgressHook 获取 workInProgressHook 对象
-
链表拼接: 将 hook.queue.pending 拼接到 current.baseQueue
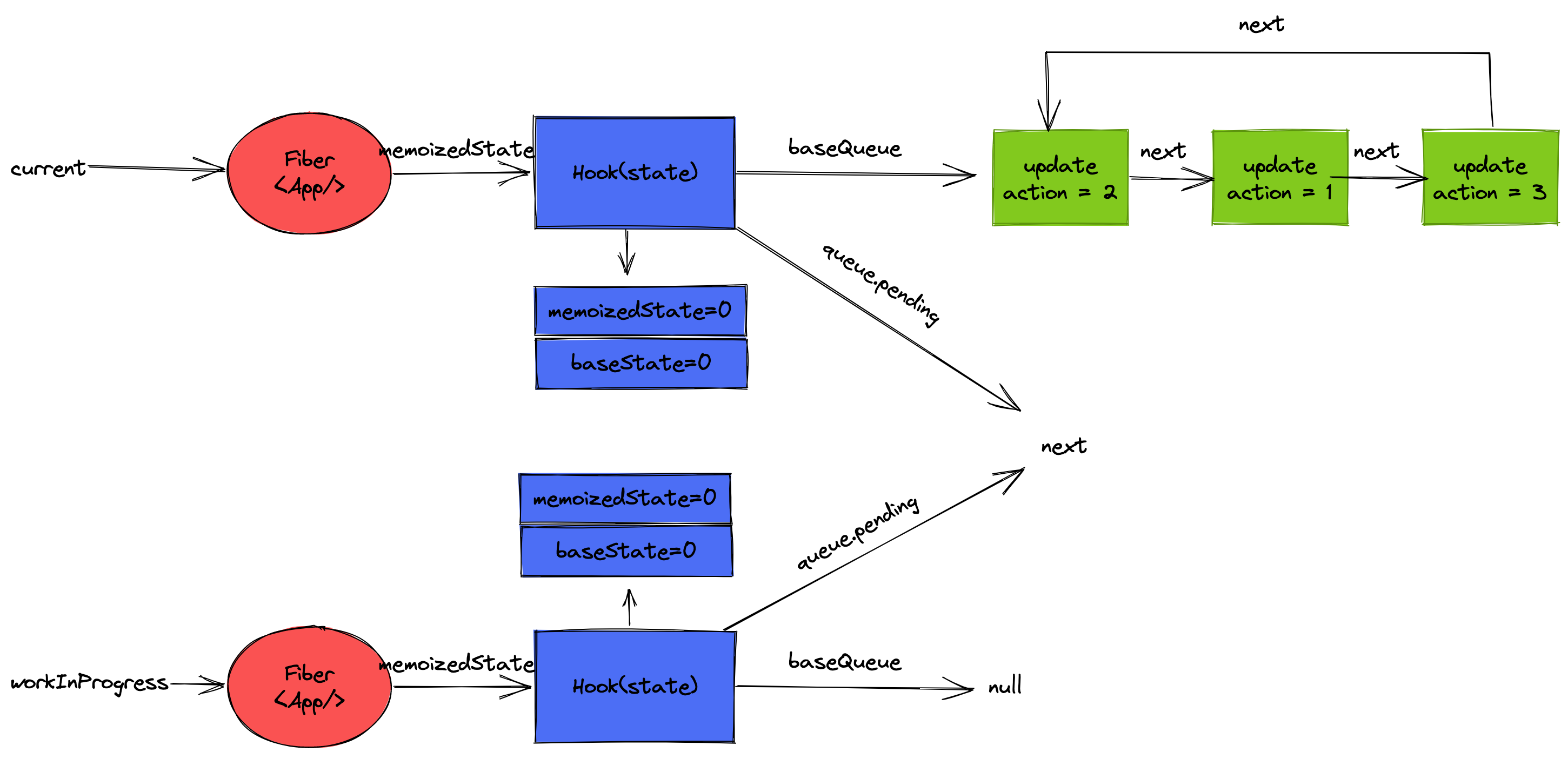
状态计算
- update 优先级不够: 加入到 baseQueue 中, 等待下一次 render
update 优先级足够: 状态合并
更新属性

性能优化
dispatchAction 函数中, 在调用 scheduleUpdateOnFiber 之前, 针对 update 对象做了性能优化.
- queue.pending 中只包含当前 update 时, 即当前 update 是 queue.pending 中的第一个 update
- 直接调用 queue.lastRenderedReducer,计算出 update 之后的 state, 记为 eagerState
- 如果 eagerState 与 currentState 相同, 则直接退出, 不用发起调度更新.
- 已经被挂载到 queue.pending 上的 update 会在下一次 render 时再次合并.
function dispatchAction<S, A>(
fiber: Fiber,
queue: UpdateQueue<S, A>,
action: A,
) {
// ...省略无关代码 ...只保留性能优化部分代码:
// 下面这个if判断, 能保证当前创建的update, 是`queue.pending`中第一个`update`. 为什么? 发起更新之后fiber.lanes会被改动(可以回顾`fiber 树构造(对比更新)`章节), 如果`fiber.lanes && alternate.lanes`没有被改动, 自然就是首个update
if (
fiber.lanes === NoLanes &&
(alternate === null || alternate.lanes === NoLanes)
) {
const lastRenderedReducer = queue.lastRenderedReducer;
if (lastRenderedReducer !== null) {
let prevDispatcher;
const currentState: S = (queue.lastRenderedState: any);
const eagerState = lastRenderedReducer(currentState, action);
// 暂存`eagerReducer`和`eagerState`, 如果在render阶段reducer==update.eagerReducer, 则可以直接使用无需再次计算
update.eagerReducer = lastRenderedReducer;
update.eagerState = eagerState;
if (is(eagerState, currentState)) {
// 快速通道, eagerState与currentState相同, 无需调度更新
// 注: update已经被添加到了queue.pending, 并没有丢弃. 之后需要更新的时候, 此update还是会起作用
return;
}
}
}
// 发起调度更新, 进入`reconciler 运作流程`中的输入阶段.
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);
}验证demo