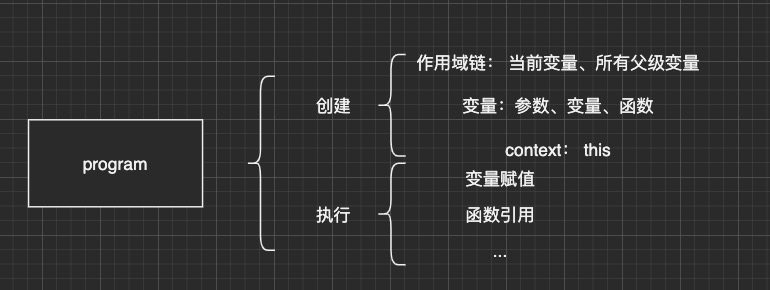
this指针、作用域
Favori,

图:Nguyen Nhut
上下文 + 作用域
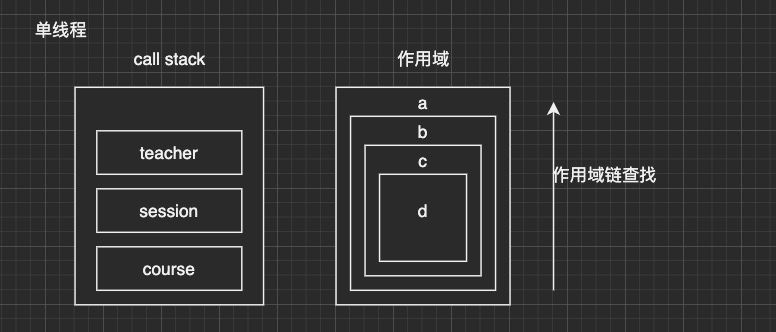
作用域链
let a = 'global';
console.log(a);
function course() {
let b = 'zhuawa';
console.log(b);
session();
function session() {
let c = 'this';
console.log(c);
teacher();
function teacher() {
let d = 'yy';
console.log(d);
// 作用域查找
console.log(b);
}
}
}
course();
// 取消了全局、块级作用域
if(true) {
let e = 1111;
console.log(e);
}this 上下文 context
this 是在执行时动态读取上下文决定的,不是在定义时决定
函数直接调用 - this 指向 window
function foo() {
console.log("函数内部的this:", this);
}
foo();隐式绑定 - this 指向调用堆栈的上一级
function fn() {
console.log("隐式绑定:", this.a);
}
const obj = {
a: 1,
};
obj.fn = fn;
obj.fn();实战:
const foo = {
bar: 10,
fn: function () {
console.log(this.bar);
console.log(this);
},
};
let fn1 = foo.fn;
fn1();
// 如何改变指向
const o1 = {
text: "o1",
fn: function () {
return this.text;
},
};
const o2 = {
text: "o2",
fn: function () {
return o1.fn();
},
};
const o3 = {
text: "o3",
fn: function () {
let fn = o1.fn;
return fn();
},
};
console.log(o1.fn());
console.log(o2.fn());
console.log(o3.fn());- 在执行函数时,如果函数被上一级所调用,那么上下文即指向上一级
- 否则为全局孤立,指向 window
将 console.log(o2.fn())结果是 o2
// 1 - 人为干涉、改变this - bind/call/apply
// 2 - 不许改变this
const o1 = {
text: "o1",
fn: function () {
return this.text;
},
};
const o2 = {
text: "o2",
fn: o1.fn,
};
// this指向最后调用他的对象,在fn执行时,函数挂到o2上即可显式绑定(bind | apply | call)
function foo() {
console.log("函数内部的this:", this);
}
foo();
foo.call({ a: 1 });
foo.apply({ a: 1 });
const bindFoo = foo.bind({ a: 1 });
bindFoo();new - this 指向的是 new 之后得到的实例
class Course {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
console.log("构造函数中的this", this);
}
test() {
console.log("类方法中的this", this);
}
}
const course = new Course("this");
course.test();异步方法中 this 有区别么
class Course {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
console.log("构造函数中的this", this);
}
test() {
console.log("类方法中的this", this);
}
asyncTest() {
console.log("异步方法外", this);
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("异步方法中的this", this);
}, 100);
}
}
const course = new Course("this");
course.test();
course.asyncTest();- 执行 setTimeout 时,传入匿名 function 执行,效果和全局执行函数效果相同
- 把 function 改为无独立上下文的箭头函数即可
bind 原理 / 手写 bind
- bind 在哪里
function sum(a, b, c) {
console.log(a, b, c, this);
return a + b + c;
}
// 1. sum.bind - 在哪里 ? => Function.prototype
//
Function.prototype.newBind = function () {
// 2. bind 是什么?
// a.返回一个函数 b. 返回原函数执行结果 c. 传参不变
const _this = this;
const args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
// args特点: 第一项 - newThis, 第二项 ~ 最后一项 - 函数传参
const newThis = args.shift();
return function () {
return _this.apply(newThis, args);
};
};- apply 应用 - 多传参数组化
Math.max(2, 4, 5, 6);
const arr = [2, 4, 5, 6];
let max = Math.max.apply(this, arr);优先级 - new > 显式 > 隐式 > 默认
function fn() {
console.log(this);
}
const obj = {
fn,
};
obj.fn(); // obj
// 显式 > 隐式
obj.fn.bind(111)();
function foo(a) {
this.a = a;
}
const obj1 = {};
var bar = foo.bind(obj1);
bar(2);
console.log(obj1.a); // 2
// new
let baz = new bar(3);
// new > 显式
console.log(obj1.a); // 2
console.log(baz.a); // 3闭包: 一个函数和他周围状态的引用捆绑在一起的组合
函数作为返回值场景
function mail() {
let content = "信";
return function () {
console.log(content);
};
}
const envelop = mail();
envelop();- 函数外部获取到了函数作用域内的变量值
函数作为参数
let content;
function envelop(fn) {
content = 1;
fn();
}
function mail() {
console.log(content);
}
envelop(mail);函数嵌套
let counter = 0;
function outerFn() {
function innerFn() {
counter++;
console.log(counter);
}
return innerFn;
}事件处理(异步执行)的闭包
let lis = document.getElementsByTagName("li");
for (var i = 0; i < lis.length; i++) {
(function (i) {
lis[i].onclick = function () {
console.log(i);
};
// setTimeout(function() {
// console.log(i);
// }, 100)
})(i);
}立即执行嵌套
(function immediateA(a) {
return (function immediateB(b) {
console.log(a); // 0
})(1);
})(0);立即执行遇上块级作用域
let count = 0;
(function immediate() {
if (count === 0) {
let count = 1;
console.log(count);
}
console.log(count);
})();拆分执行 多个闭包
function createIncrement() {
let count = 0;
function increment() {
count++;
}
let message = `count is ${count}`;
function log() {
console.log(message);
}
return [increment, log];
}
const [increment, log] = createIncrement();
increment();
increment();
increment();
log(); // count is 0实现私有变量
function createStack() {
return {
items: [],
push(item) {
this.items.push(item);
},
};
}
const stack = {
items: [],
push: function () {},
};
function createStack() {
const items = [];
return {
push(item) {
items.push(item);
},
};
}